The antibiotics We are finished while the data on in -hospital infections in our country remain heartbreaking. Despite the measures taken in the direction of dealing with this serious problem, resistance to germs It costs thousands of deaths in Intensive Care Units (ICU).
According to official data from EDY from the 2000 by 2018 The antibiotic pathogen resistance in Greece increased by 46%, while only 2020 we had almost 41,000 infections From multi -resistant germs, recording a 76% increase compared to 2016.
Greek doctors raise their hands high and declare how they no longer have strong ‘arms»In their quiver to fight powerful germs and bacteria endemic to Greek hospitals, such as Asinomemacter, Clebsiella and the pseudomonas.
Effectively – at least – antibiotics, such as carbapenemes, third -generation cephalosporins and fluoroquinolones are currently resistant to the powerly germs.
‘At war This the germs prove to be very stronger Human, “said Professor of Pathology of Infectious Diseases at the Nursing School of Nursing, Nikolaos Sypsas, noting that the problem remains, despite the institutionalization of the control of the use of antibiotics with electronic prescription.
Did not even rule out an additional measure of control control, to be instituted mandatory antibiogram In hospitals before antibiotic administration.
Professor of Sypeas: The end of antibiotics and the impacts in Greece
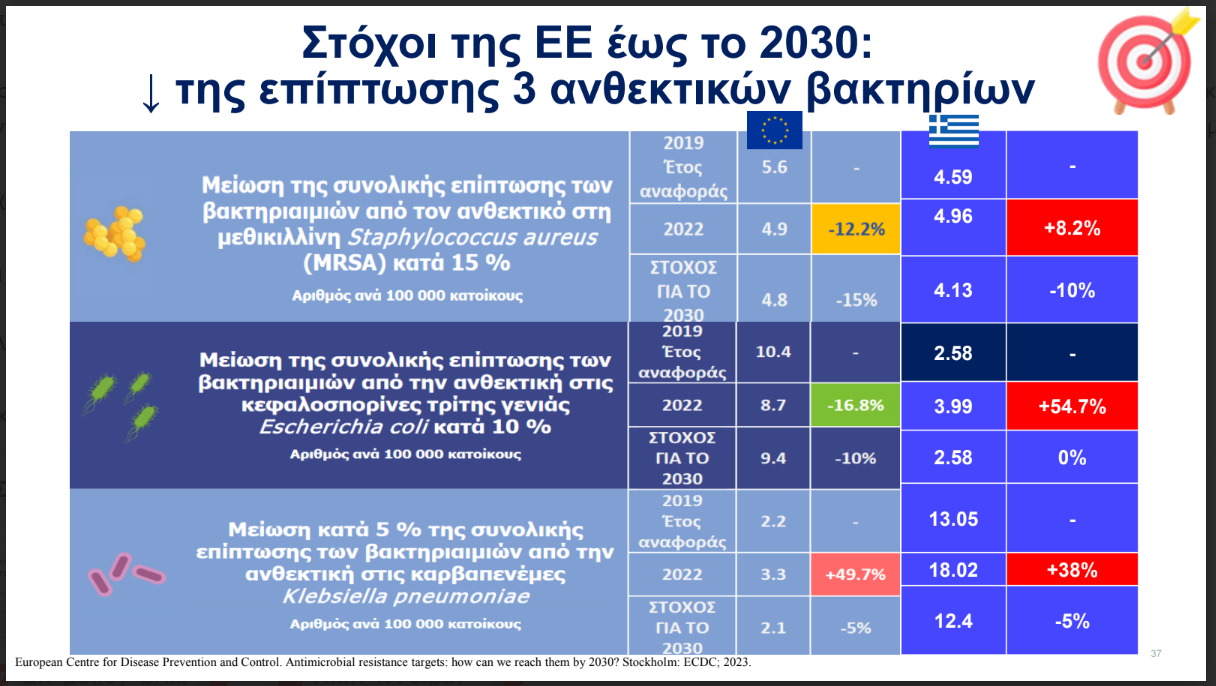
In his speech at a scientific and informative meeting entitled, “The Treatment of Microbial Strength and the Value of Modern Antibiotics”, the professor pointed out that the problem is pan -European and worldhowever, Greece remains in adverse and more vulnerable to Europe in the prevalence of inpatient infections.
According to official data of 2023 in hospital pathogens our country is Negative ‘champion’with twice as many EU average, health -related infections (LSI).


In dramatic Tons of the Professor and President of the Hellenic Infectious Disease Society, Mr. Compactpointed out how antibiotics, which make up key drugs Modern medicine, they lose their strength against bacteria that adapt and evolve.
‘We have to realize that antibiotics they finished. In essence, there is no new antibiotic. And why is there no new antibiotic? Why We destroyed What we had and because no pharmaceutical company is investing, because the cost is too high for new antibiotics to come out, “the scientist said.
Greece under Europe’s microscope
The picture presented by Professor Nikos Sypas is’dark»: Greece is 1st in the European Union in consumption of antibiotics in the community and 6th in the inpatient consumption.
Germs such as Klebsiella Pneumoniae, Acinetobacter Baumannii and Pseudomonas Aeruginosa show multiple antibiotic resistance in Greek hospitals, limiting dramatically therapeutic options.
This situation led to the ECDC to conduct an autopsy with experts in Greek hospitals just a year ago and then issue a directive in 2024 to the rest of Europe. The report characterized Greece ‘unsafe place for patients“(” Unsafe part for patients “) and at the same time recommended the preventive isolation Patients returning from hospitalization to Greece due to the risk of transmission of multi -resistant pathogens.
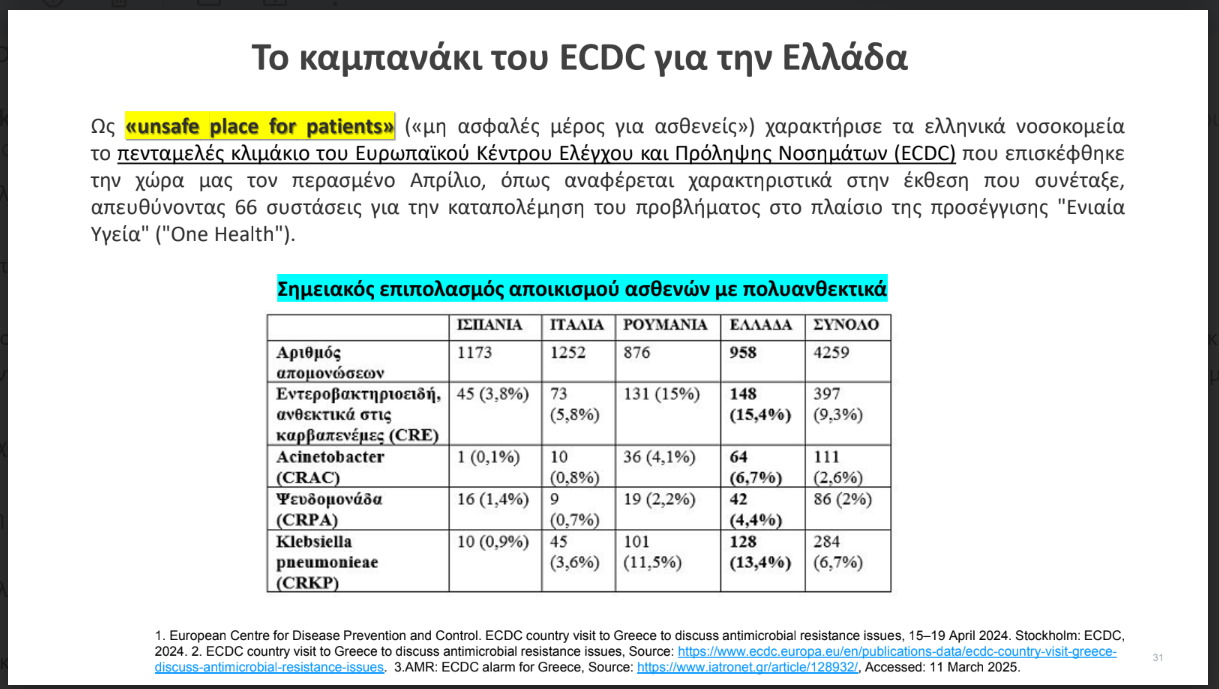

According to Professor Sypsa, in addition to heavy blood tax and higher mortality, infections of resistant bacteria lead to prolonged hospitalizationincreased cost care and heavier complications .
In many cases, doctors are forced to return to old, toxic or less effective drugs.
The deadlock with the new antibiotics
In this unfavorable environment, the need for innovative antibiotics is imperative. However, the International Innovation Production System in this area has crashed. And the reason is simple: There is no financial motivationas the professor pointed out.
The development of a new antibiotic touches the Astronomical amount of $ 1.5 billion And, due to the right restrictions on use (to prevent further strength), the revenue is minimal. Many companies that developed successful new antibiotics then went bankrupt.
The new antibiotics, according to Professor of Pathology, Vassilis Grammelis, manage to reduce mortality from 35% to 5%, which means how using them We could avoid, 3 out of 10 patient deaths.
However, as he said, ‘Since the 1980s onwards no new category of antibiotics has come outthat is, based on a new way of action against germs. As a result, germs are crossing immunity and being strengthened against existing antibiotics, “Mr Grammelis said.
The problem is multifaceted, according to Professor Sypsas: on the one hand No new drugs producedor new innovative antibiotics have not been honored to be released in our country and imported with the “dropper” through IFET and AEO, while on the other hand, cheap and valuable antibiotics for patients not produced by companies due to lack Economic incentive.
‘The government is required to develop a serious strategic plan for the development and import Antibiotics to strengthen our country’s efforts in this area, “said EEL President, Mr. Sypeas.

The need for motivation
In Europe we count each year 35,000 deathsnumber comparable to that of influenza, tuberculosis and HIV/AIDS together. At the same time, the annual healthcare cost and productivity losses due to microbial strength being estimated at 1.5 billion euros, while the corresponding cost of microbial strength in Greece (EHR – annual health costs) is over € 42 million.
According to the Antonis FosterPfizer’s Director Policy & Public Affairs, the problem is so large that the only solution seems to be incentives to make this situation more viable.
Thus, the international scientific community, as he pointed out, now proposes the so -called Pull Incedes: Economic Models, that is, that, that is, reimburse The development of a new antibiotic regardless of its sales (eg through subscription models).
They are essentially, compensation mechanisms that reward pharmaceutical companies for the successful development new antibiotics, regardless of sales.
Successful examples are the Sweden and United Kingdomcountries that have already adopted such models, with positive results.
Another proposed solution, according to Mr Fousseris, who is being discussed in the context of the revision of EU pharmaceutical legislation is also the establish voucher.
“Voucher is essentially an incentive for a company that will discover an antibiotic, so that – whether for this antibiotic or, for another medicine – to increase its patent over a period of time. European Commission’s proposal is 12 months. This is considered a good incentive for companies to be able to do work, “he concluded.
If they are not taken timely Measures, as scientists have pointed out in dramatic tones, is predicted in 2050 to occur worldwide 10 million deaths per year and to have financial costs 100 trillion dollars.
Source: Iaropedia.gr
